Integrating weight data is tough. Mismatched connections cause frustrating errors and delays. An RS232 scale offers a simple, reliable solution for seamless data transfer into your systems.
An RS232 scale is an electronic scale equipped with a standard RS232 serial communication port. This interface allows the scale to connect directly to devices like computers, printers, or PLCs, enabling reliable, two-way transfer of weight data and control commands for system integration.
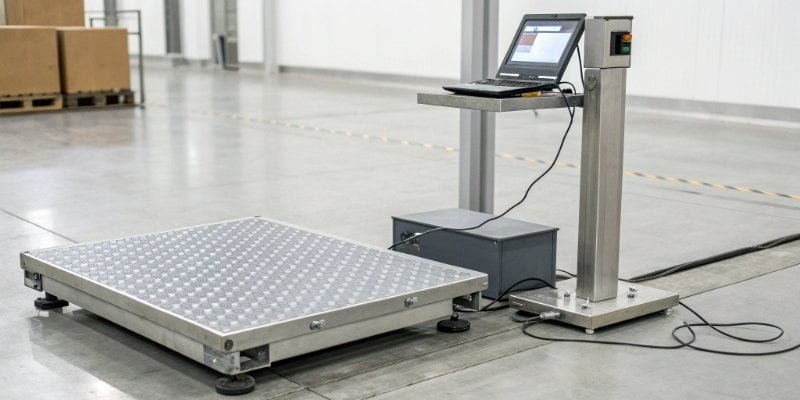

So, you know an RS232 scale1 is about connection. But what does "RS-232" actually mean, and why does this decades-old standard still matter so much in modern industrial automation2? The name itself holds the key to its reliability. Let’s dive into the specifics, because understanding the "how" is crucial for any technical director or purchasing manager looking to make a smart investment. The details might surprise you.
What does RS-232 stand for?
Confused by technical jargon like RS-232? It can feel like a barrier in important discussions. Understanding this term is simple and gives you the confidence to talk tech.
RS-232 stands for "Recommended Standard 232." It is a long-established standard for serial communication, defining the electrical characteristics and timing of signals. It was created by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) to ensure different manufacturers' equipment could communicate reliably with each other.
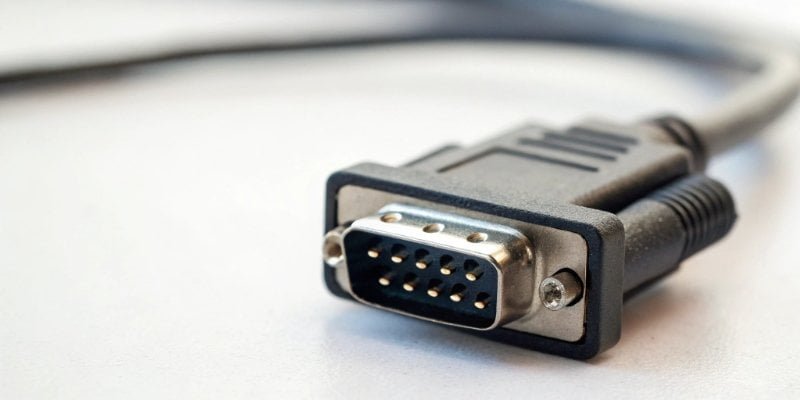

The name "Recommended Standard 2323" highlights its primary purpose: standardization. Before its creation, connecting devices was chaotic. The Electronic Industries Alliance4 (EIA) established RS-232 to ensure equipment from different vendors could communicate reliably. It governs serial communication, where data is sent one bit at a time over a wire. This simple, robust method is perfect for sending precise weight data from a scale to a computer or controller. It removes guesswork from integration. As a company with 19 years of experience, we've seen firsthand how this standard simplifies projects for our software partners. Modern scales typically use a 9-pin (DB9) connector for this. Its most critical pins for simple data transfer are:
| Pin | Signal Name | Function for the Scale |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | RXD (Receive Data) | Receives commands from a host (e.g., PC). |
| 3 | TXD (Transmit Data) | Transmits weight data to the host. |
| 5 | GND (Signal Ground) | Provides a common ground reference. |
This clear definition is why RS-232 has been a trusted interface in industrial settings for decades.
What are the levels of RS-232?
Digital signals aren't just ones and zeros. Incorrect voltage levels can cause communication failures or damage equipment. RS-232 uses a specific, robust voltage system to guarantee clear signals.
RS-232 uses specific voltage levels for data. A logic '0' (called a "space") is a positive voltage between +3V and +25V. A logic '1' (a "mark") is a negative voltage between -3V and -25V. This high voltage swing ensures noise immunity in industrial environments.
The voltage levels5 of RS-232 are a key reason for its longevity in industrial settings. Unlike the Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) common inside computers, RS-232 uses a much larger voltage range. This is by design. The area between -3V and +3V is an undefined buffer zone, which helps prevent false readings. The high voltage swing makes the signal highly resistant to electrical noise, something that is very common in factories with large motors and machinery. A small voltage spike that might corrupt a 5V TTL signal would barely register on a +/-12V RS-232 signal. As a technical director, this means you can trust the data integrity6 from an RS-232 scale, even over longer cable runs7 (up to 15 meters/50 feet).
| Specification | RS-232 | TTL (Typical) |
|---|---|---|
| Logic '1' Voltage | -3V to -25V ('Mark') | +2V to +5V |
| Logic '0' Voltage | +3V to +25V ('Space') | 0V to +0.8V |
| Noise Margin | High | Low |
This robust electrical design is fundamental to the reliability we promise our clients at Weigherps.
How to measure RS-232 signal?
A scale connection fails, and you're stuck guessing the cause. Is it the cable, the scale, or the computer? Simple tools and a clear method can pinpoint the problem fast.
To measure an RS-232 signal, you can use a multimeter to check for the negative idle voltage (around -10V) on the Transmit (TXD) pin. For seeing the actual data, a serial port monitoring software on a PC is invaluable. For advanced troubleshooting, an oscilloscope is best.

When an RS-232 scale isn't communicating, a systematic approach is best. As an engineer myself, this is how I tackle it, and how our support team guides our clients.
1. Basic Check with a Multimeter
This is your first line of defense. Set your multimeter8 to DC Volts. Place the black probe on the Ground pin (pin 5) and the red probe on the Transmit Data (TXD) pin (pin 3) of the scale's connector. When the scale is on but idle, you should measure a steady negative voltage, typically between -5V and -12V. This confirms the scale is powered and the port is active. If you see 0V or a positive voltage, there’s a problem with the scale's port.
2. Viewing Data with a Serial Monitor
If the voltage check passes, the next step is to see if data is being sent. Use a PC with a serial port (or a USB-to-Serial adapter) and run a serial monitor program like PuTTY or RealTerm. Match the baud rate, data bits, and parity settings to the scale's configuration. You should see a stream of characters representing the weight data appearing on your screen.
3. Advanced Analysis with an Oscilloscope
For complex issues like signal degradation or timing errors, an oscilloscope9 is the ultimate tool. It lets you visually inspect the waveform, confirming the correct voltage levels, bit timing (baud rate), and signal integrity. This is rarely needed but is the definitive way to diagnose hardware-level communication problems.
Is RS-232 still relevant today?
With modern interfaces like USB and Ethernet, RS-232 can seem obsolete. You might overlook it, but that would be a mistake. This "old" technology remains critical for industrial applications.
Yes, RS-232 is highly relevant today, especially in industrial automation, lab equipment, and retail POS systems. Its strengths are simplicity, high noise immunity, and point-to-point reliability. For low-speed, mission-critical data like weight readings, it is often more robust and cost-effective than complex network interfaces.

In our 19 years of manufacturing industrial scales, I’ve seen many technologies come and go. RS-232 stays. While USB and Ethernet dominate consumer electronics, the industrial world has different priorities. RS-232 provides a direct, simple, point-to-point connection that is incredibly robust. There are no complex drivers to install, no IP addresses to configure, and no network switches to fail. This simplicity is a feature, not a limitation. For an application like getting a weight reading from a scale to a controller a few meters away, it is the perfect tool for the job. It's predictable and reliable, which is exactly what you need when production uptime is critical.
| Feature | RS-232 | USB | Ethernet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Low (Point-to-Point) | Medium (Host/Device) | High (Networked) |
| Noise Immunity | High | Low | Medium (with shielding) |
| Max Distance | ~15 meters | ~5 meters | 100 meters |
| Use Case | Simple, reliable data | Peripherals, high speed | Networked devices |
For software vendors integrating our scales, the benefit is clear: a stable, easy-to-program interface that reduces development time and support calls.
Conclusion
In short, an RS232 scale is your reliable partner for accurate data integration. Its proven simplicity and robustness make it an essential, cost-effective tool in any modern industrial system.
-
Explore this link to understand how RS232 scales facilitate seamless data transfer in industrial applications. ↩
-
Understand the role of automation in enhancing efficiency and reliability in industrial processes. ↩
-
Gain insights into the historical context and importance of the RS-232 standard in communication. ↩
-
Understand the role of the EIA in establishing communication standards like RS-232. ↩
-
Explore how voltage levels in RS-232 ensure reliable data transmission in noisy environments. ↩
-
Explore the concept of data integrity and its significance in industrial applications. ↩
-
Understand the practical limitations of RS-232 cable runs and their implications for installation. ↩
-
Find out how to effectively use a multimeter for troubleshooting RS-232 connections. ↩
-
Explore the advanced capabilities of oscilloscopes in diagnosing communication issues. ↩





Comments (0)